Nature has been the world’s greatest innovator and problem solver for millions of years. The natural world is a treasure trove of ingenious designs, efficient processes, and sustainable solutions that have evolved through trial and error. Biomimicry, also known as biomimetics, is the field of science and engineering that draws inspiration from nature’s innovations to solve human challenges. It involves studying and emulating nature’s forms, processes, and systems to create sustainable and efficient solutions across various industries. This article delves into the fascinating world of biomimicry, exploring its principles, applications, and the remarkable examples of nature’s innovations that continue to inspire human technological advancements.
Principles of Biomimicry:
Biomimicry is guided by several key principles that help researchers and engineers unlock nature’s secrets for innovation:
Emulating Nature’s Forms: Nature’s diverse range of structures, from the microscopic to the macroscopic, provide inspiration for human design. Examples include the lotus leaf’s self-cleaning surface, which has influenced the creation of dirt- and water-resistant coatings, and the honeycomb structure found in beehives, which has been applied to architectural design for its strength and efficiency.
Harnessing Nature’s Processes: Nature has perfected numerous processes over time, such as photosynthesis, efficient energy conversion, and self-healing mechanisms. These processes inspire the development of sustainable energy solutions, improved manufacturing techniques, and advanced materials with self-repairing capabilities.
Adapting to Environmental Constraints: Organisms have evolved to thrive in diverse environments, making them experts in adapting to constraints such as limited resources, extreme temperatures, and harsh conditions. By studying how organisms overcome these challenges, engineers can develop solutions for sustainable resource management, energy efficiency, and resilience in the face of climate change.
Applications of Biomimicry:
Biomimicry finds applications in a wide range of fields, including:
Architecture and Design: Architects draw inspiration from nature’s aesthetics, forms, and structural principles to create buildings that are not only visually appealing but also energy-efficient and sustainable. Examples include the Eastgate Centre in Zimbabwe, inspired by termite mounds for natural ventilation, and the Eden Project in the UK, based on the geometry of soap bubbles for efficient use of materials.
Engineering and Materials Science: Nature’s materials, such as spider silk, lotus-inspired surfaces, and bone structure, have inspired the development of lightweight and strong materials, water-repellent surfaces, and more efficient manufacturing techniques. These innovations have applications in the aerospace, automotive, and consumer goods industries.
Energy and Sustainability: Biomimicry plays a crucial role in developing renewable energy technologies and sustainable resource management strategies. Efforts are underway to emulate photosynthesis for efficient solar energy conversion, mimic bird flight for improved wind turbine design, and replicate the water conservation mechanisms of desert plants for sustainable agriculture.
Medicine and Healthcare: Nature provides a wealth of inspiration for medical advancements. Researchers study the intricate systems of organisms to develop new drug delivery methods, tissue engineering techniques, and biomaterials. Examples include the development of Velcro-inspired bandages and gecko-inspired adhesives for medical applications.
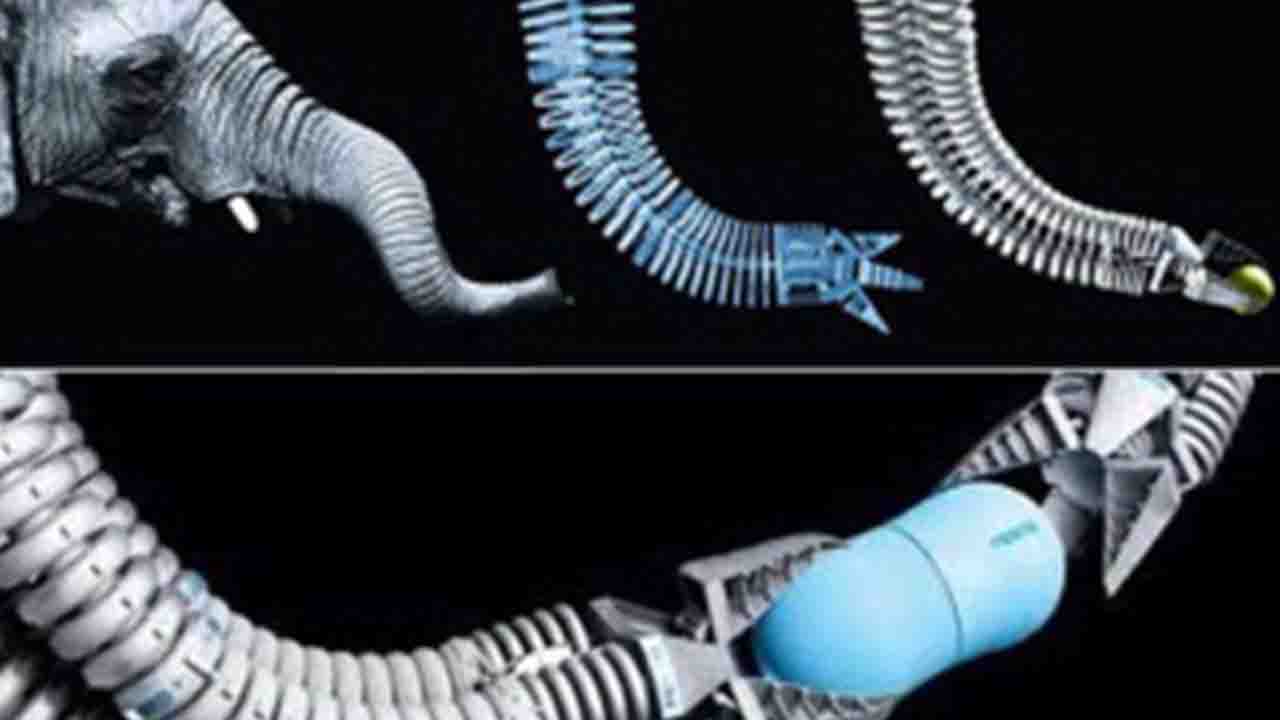
Transportation and Robotics: By studying animal locomotion, engineers have developed efficient propulsion systems, like fish-inspired underwater robots and bird-inspired aircraft wings. Biomimetic robots are also being designed to navigate challenging terrains, aiding search and rescue missions or exploring hazardous environments.
Remarkable Examples:
Nature’s innovations continue to astonish and inspire scientists and engineers worldwide. Here are a few remarkable examples:
- Velcro: Inspired by the burrs that stick to clothing and animal fur, Swiss engineer George de Mestral invented Velcro, a hook-and-loop fastening system widely used today.
- Shinkansen Bullet Train: The design of the Shinkansen, Japan’s high-speed train, was inspired by the kingfisher bird’s streamlined shape, reducing noise and energy consumption.
- Whale-Inspired Wind Turbines: The tubercles on humpback whale fins inspired wind turbine blade designs that increase efficiency, reduce noise, and minimize the risk of bird collisions.
- Termite Mounds: The efficient ventilation system of termite mounds inspired the design of the Eastgate Centre in Zimbabwe, reducing energy consumption by 90% compared to traditional air-conditioned buildings.
- Gecko-Inspired Adhesives: By studying the adhesive properties of gecko feet, scientists have developed dry adhesives that enable robots to climb walls and ceilings, with potential applications in space exploration and rescue missions.
Nature’s innovations through billions of years of evolution have yielded remarkable solutions to countless challenges. Biomimicry harnesses this vast knowledge to inspire sustainable and efficient solutions in various fields. From architecture and design to engineering, energy, medicine, and transportation, biomimicry has the potential to revolutionize industries and drive the transition to a more sustainable future. By looking to nature, we can tap into an endless source of inspiration, learning from the world’s greatest innovator: Mother Nature herself.