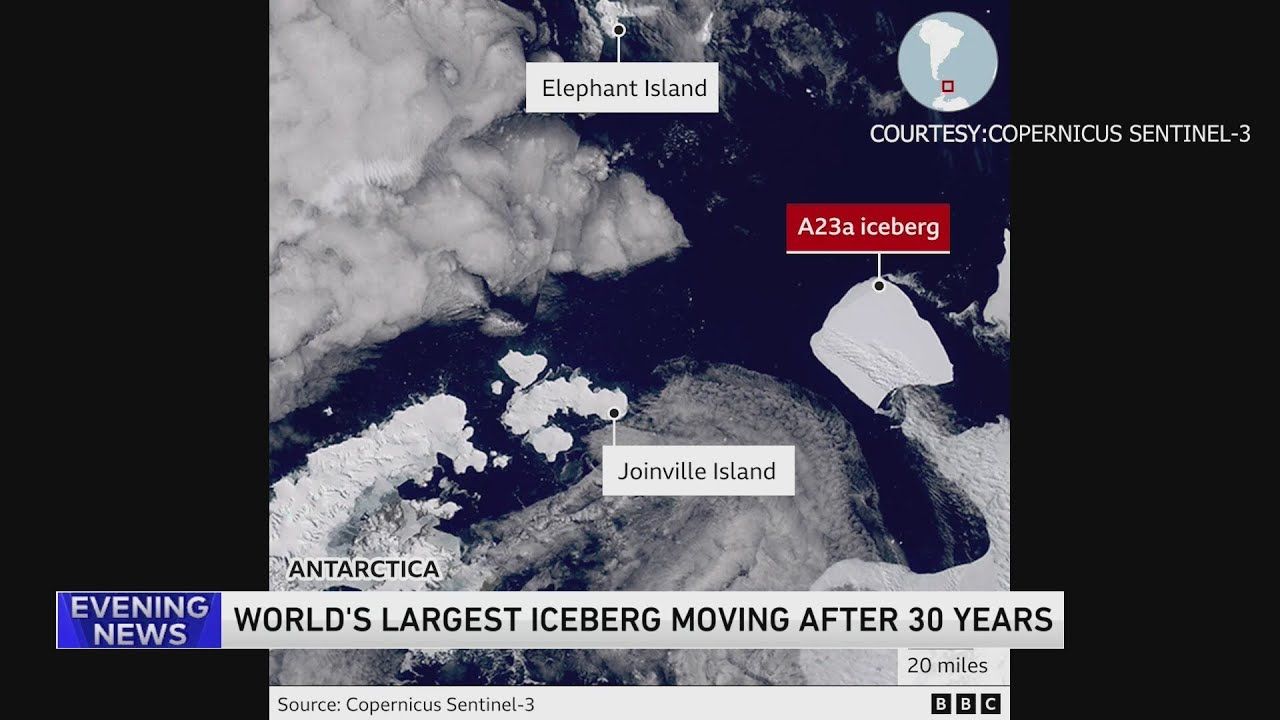
In a remarkable turn of events, the colossal iceberg known as A23a, measuring a staggering 4,000 square kilometers (1,500 square miles) and surpassing the size of both New York City and Greater London, has finally broken free from its grounded state in Antarctic waters. According to the British Antarctic Survey, the iceberg had been lodged on the ocean floor since its detachment from the Filchner Ice Shelf in 1986.
This monumental iceberg, a frozen behemoth three times the size of New York City, had long captivated scientists and researchers, symbolizing both the resilience and fragility of Antarctica’s icy landscapes. Dr. Keith Makinson of the British Antarctic Survey commented on the unexpected development, stating, “I asked a couple of colleagues about this, wondering if there was any possible change in shelf water temperatures that might have provoked it, but the consensus is the time had just come.”
The iceberg’s prolonged grounding for over three decades had left experts speculating about its eventual fate. Simon Fleming, a glaciologist at the British Antarctic Survey, noted that the iceberg’s size was gradually diminishing over the years, and it was only a matter of time before it would lose its grip on the ocean floor and set itself adrift.
In a surprising revelation, Fleming observed the first signs of movement from the colossal A23a iceberg in 2020. This gradual dislodging marked the beginning of its journey beyond the confines of the Weddell Sea. The British Antarctic Survey has confirmed that A23a is now ungrounded and is steadily making its way along ocean currents toward the sub-Antarctic region of South Georgia.
The newfound mobility of A23a raises intriguing questions among scientists about the potential implications for the surrounding ecosystem and climate. As the iceberg navigates its path, scientists will closely monitor its trajectory, examining the dynamic interplay between ice, ocean currents, and environmental conditions.
This unprecedented event underscores the ever-changing nature of Antarctica’s ice formations and prompts a deeper exploration into the forces that govern these colossal structures. As A23a ventures beyond Antarctic waters, it leaves a frozen legacy that extends beyond its sheer size, offering scientists a unique opportunity to study the intricate dance between icebergs and the polar environment.