Cancer is a serious health issue that not only has an impact on the health and happiness of patients and their loved ones, but also has a significant financial impact on the nation’s health care system. There is now a rising cancer incidence in Sri Lanka with nearly 37,753 new cases of cancer diagnosed in the year 2021 with a crude incidence rate (CR) of 170.4 per 100,000 population.

Determining if cancer has been cured after therapy involves several factors and considerations. As cancer detection methods are continually evolving with advancements in technology and medical research, currently there are several ways to detect a malignant tumor.
One such method is liquid biopsy which is gaining traction as a less invasive method for detecting cancer. This technique involves analyzing circulating tumor cells (CTCs), cell-free DNA (cfDNA), or other biomarkers present in bodily fluids like blood or urine. It can provide information about tumor genetics and monitor treatment response.
At present, Artificial Intelligence (AI) and machine learning algorithms are also being integrated into various aspects of cancer detection, including image analysis, genetic profiling, and data interpretation. Moreover there is Multiparametric imaging techniques that combine different imaging modalities such as MRI, PET, and CT scans to provide a comprehensive assessment of tumors. By integrating multiple types of data, these approaches can improve diagnostic accuracy and help tailor treatment plans to individual patients.
Researchers are also continually searching for new biomarkers that can detect cancer at its earliest stages when treatment is most effective. Recent studies have identified promising biomarkers in blood, saliva, and other bodily fluids that could potentially be used for early cancer detection.
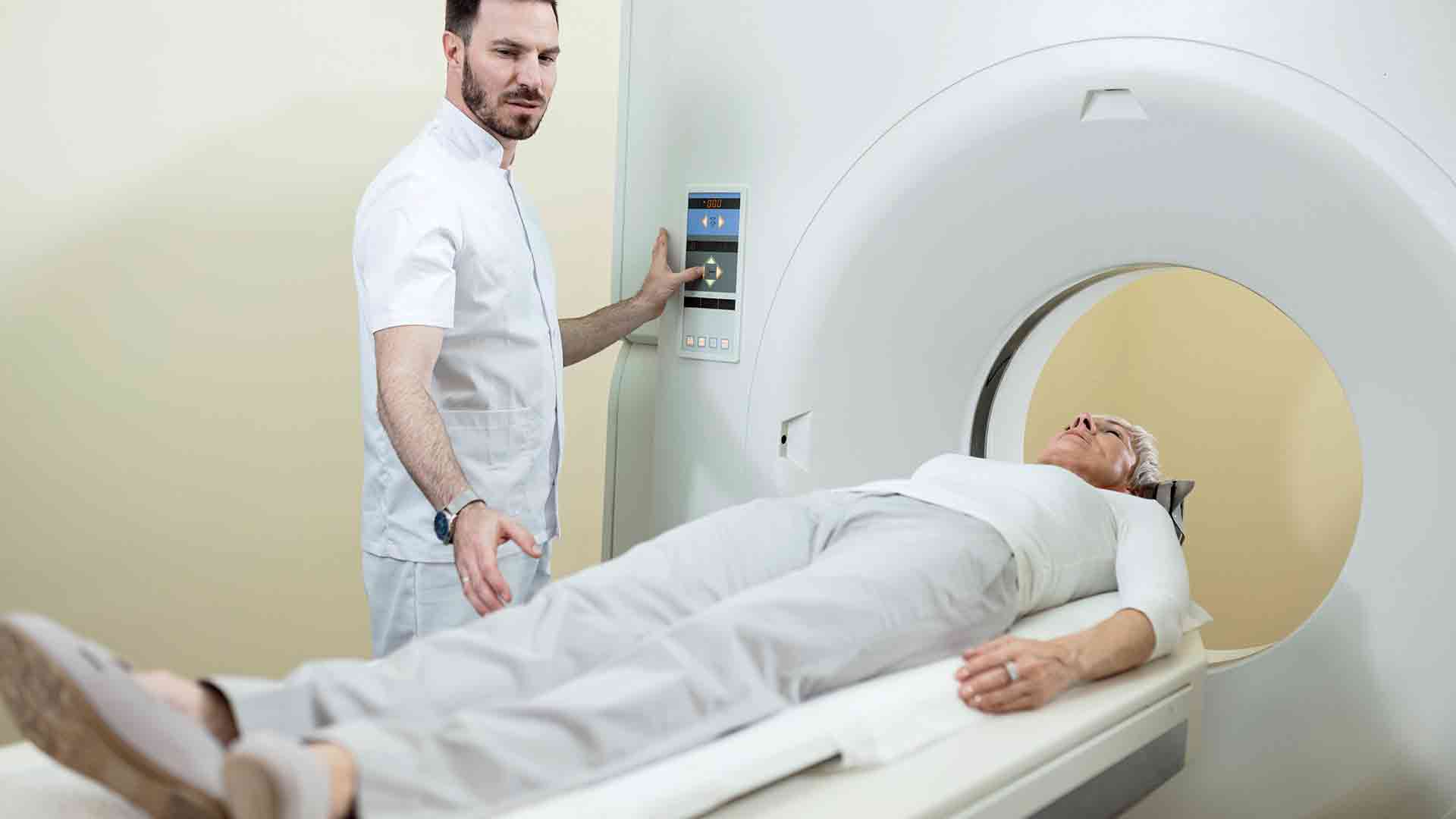
There are several other cancer detection methods and it will keep evolving in future, yet the one of the most accurate method used in world is PET CT Scans.
PET-CT Scans (Positron Emission Tomography) are the latest way to assess whether cancer treatment has been successful. Imaging studies such as PET CT scans can show if tumors have shrunk, disappeared, or remained stable after treatment. These tests can provide valuable information about the response to treatment.
PET-CT Scans are used to determine if solid cancers that form as tumors in tissues such as the breast, lung, prostate, and colon are cured. PET-CT Scans are also used to monitor Lymphomas which are cancers that start in cells of the lymphatic system, which is part of the body’s immune system.
PET-CT Scan Process
PET scans are a type of imaging test that uses a radioactive tracer to show how tissues and organs are functioning. A small amount of a radioactive tracer, usually a type of sugar called FDG (fluorodeoxyglucose), is injected into a vein. Cancer cells are typically more metabolically active than normal cells and consume more glucose. The FDG tracer is taken up by these active cells. A PET CT scanner detects the radioactive tracer and creates images that show where the tracer is in the body. Areas with higher tracer uptake often indicate areas of high metabolic activity, which can be a sign of cancer.
Can a scan detect small cancerous tumors?
PET-CT scan is capable of detecting even small cancerous tumors. As PET CT scans are highly sensitive imaging tests it can identify areas of abnormal metabolic activity in the body, which is often indicative of cancer cells. However, PET CT Scan can detect tumors approximately above 5-10 millimeters in diameter which made of about one million cell clusters. Tumors lesser than 5 millimeters or one million cell clusters are difficult to differentiate through these scans as they are microscopic.
Combining PET with CT (or MRI) improves the accuracy of the scan. CT provides detailed structural information, helping to precisely locate the abnormal metabolic activity seen on the PET scan.
Post-treatment follow-up
An essential part of cancer care is post-treatment follow-up. In order to make sure the cancer has not returned or recurred and to control any possible adverse effects of treatment, it entails routine check-ups, tests, and monitoring. The type of cancer, its stage, the treatments taken, and the unique characteristics of each patient can all affect the details of follow-up care.
After treatment, patients are usually scheduled for regular follow-up appointments which include physical exams, blood tests, and imaging scans to monitor for any signs of cancer recurrence.