Synthetic biology is a rapidly growing field that is using engineering principles to design and build new biological systems. This can be used to create new products and services, improve existing ones, and solve some of the world’s most pressing problems.
One of the most exciting potential applications of synthetic biology is in the development of new medicines. Synthetic biologists are working to create new drugs that are more effective and less harmful than existing ones. They are also working to develop new ways to deliver drugs to the body, such as by using bacteria to create “living drugs” that can target specific cells or tissues.
Another promising area of research is in the development of new biofuels. Synthetic biologists are working to create new bacteria that can produce biofuels from renewable resources, such as algae or agricultural waste. This could help to reduce our reliance on fossil fuels and reduce greenhouse gas emissions.
Synthetic biology is also being used to develop new ways to clean up pollution. For example, synthetic biologists are working to create bacteria that can break down pollutants in wastewater or soil. This could help to improve the environment and protect human health.
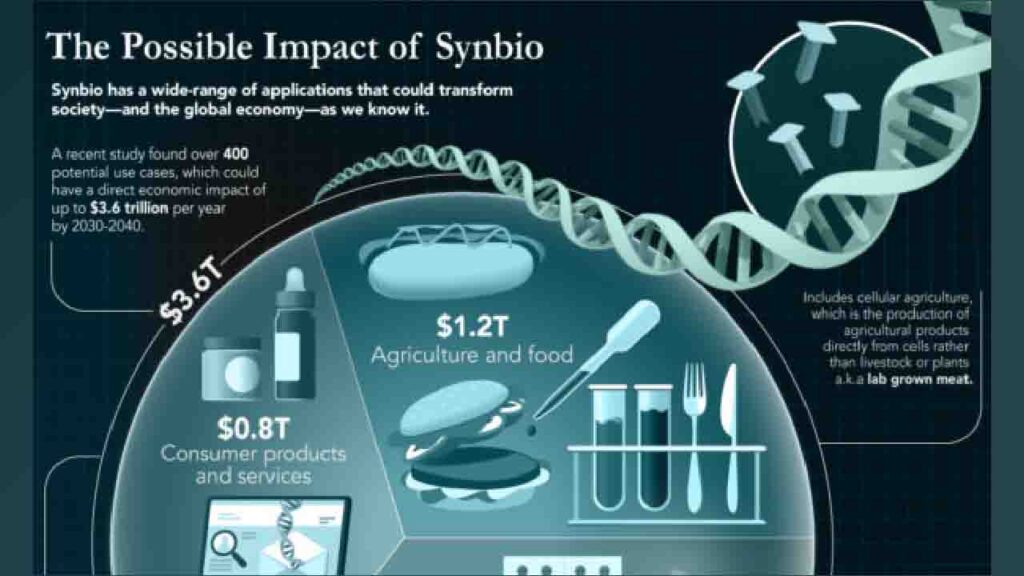
In addition to these specific applications, synthetic biology has the potential to revolutionize many other industries, including agriculture, food production, and materials science. As the field continues to develop, we can expect to see even more innovative and groundbreaking applications of synthetic biology in the years to come.
Here are some specific examples of how synthetic biology is being used to address some of the world’s most pressing problems:
Developing new medicines: Synthetic biologists are working to create new drugs that are more effective and less harmful than existing ones. For example, researchers at the University of California, Berkeley, have created a new type of antibiotic that is effective against drug-resistant bacteria.
Developing new biofuels: Synthetic biologists are working to create new bacteria that can produce biofuels from renewable resources, such as algae or agricultural waste. For example, researchers at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology have created a new strain of algae that can produce biodiesel.
Cleaning up pollution: Synthetic biologists are working to create new ways to clean up pollution. For example, researchers at the University of Washington have created a new type of bacteria that can break down pollutants in wastewater.
These are just a few examples of the many ways that synthetic biology is being used to address some of the world’s most pressing problems. As the field continues to develop, we can expect to see even more innovative and groundbreaking applications of synthetic biology in the years to come.
Here are some of the challenges that synthetic biologists are facing:
- Safety: One of the biggest challenges facing synthetic biologists is ensuring the safety of their products. Synthetic biology can be used to create new organisms that have never existed before, and it is important to make sure that these organisms are safe before they are released into the environment.
- Regulation: Another challenge facing synthetic biologists is regulation. Many countries have not yet developed regulations for synthetic biology, and this can make it difficult for synthetic biologists to get their products to market.
- Public acceptance: Synthetic biology is a relatively new field, and there is still some public uncertainty about its safety and ethics. Synthetic biologists need to work to educate the public about the potential benefits of synthetic biology and to address any concerns that people may have.
Despite these challenges, synthetic biology is a rapidly growing field with the potential to revolutionize many industries and solve some of the world’s most pressing problems. As the field continues to develop, we can expect to see even more innovative and groundbreaking applications of synthetic biology in the years to come.
















